Electrical Machine for GATE ESE PSU’s Exams
Welcome to Neospark by Gatematic. Today we are going to discuss how to prepare Electrical Machines for GATE and ESE. At the onset, I would like to tell you that recently in Gate 2021, the syllabus has changed in a few areas but Electrical Machines is unchanged. The same syllabus that was proposed in 2016 still holds true. However, the topics single phase transformer and 3 phase induction motor have been incorporated in the GATE IN syllabus from 2021 onwards. EE Aspirants are advised to read the entire blog. However, IN aspirants can only see the above-mentioned 2 modules after the introduction.
Electrical Machines is one of the most important subjects for a graduate in EE and it is essential for every graduate to have a thorough idea about this subject as even after GATE or ESE, you can expect interviewers to grill you on this subject in interviews for MTech, PSU, BARC, ISRO, etc. So if any aspirant wants to skip this subject, they would be making a fatal mistake. Further, you can safely assume an average of 10-12 marks from this subject in GATE EE paper which accounts for almost 10% and shouldn’t be taken lightly. Both subject clarity and problem-solving ability play a role in this subject. This is a subject that can make the difference between a top 100 rank and a top 1000 rank for both EE and IN. In particular, an IN aspirant who can master the corresponding portions of machines can gain a huge advantage over their competitors.
The necessary prerequisite for starting Machines is that a student should have covered Network Theory properly irrespective if you are from EE or IN. The most important topics with respect to machines would be Network Theorems, AC circuits with phasor diagrams, 3-phase systems, and magnetically coupled circuits. Apart from that although not necessary a basic idea of Electrical Engineering materials would prove useful. ESE aspirants already study it as a separate subject. Also, a brief knowledge of Electromagnetic Theory is needed in particular Lorentz’s force law and Lenz’s law along with basic magnetostatics. However, users of Neospark Paid Course need not worry about them. The necessary prerequisites have already been covered very well in the course by Sohail Sir. One can enroll in the course as a live class of Machine is going to start from 25th September. If missed then you can watch the recorded one. To know in detail. Watch this video:
|
|
They should focus on completing Network theory before starting Machines.
References for the studying Electrical Machines for a self-study student are:
- Electrical Machines by Nagrath and Kothari – Best for brief and concise explanation to the point
- Electrical Machinery by P.S. Bimbhra – A second source should someone want to refer but some parts are unnecessarily elaborated here making it monotonous. This book is however very good if someone wants to see solved examples.
- Generalized Theory of Electrical Machines by P.S. Bimbhra – Some topics which are not found in the previously mentioned books can be found here.
- GATE Electrical Engineering Previous year Book
 |
Electrical machines are also a prerequisite for Electric Drives which is in the ESE syllabus. Also although Machines is not needed to for studying Power Electronics, good questions can be framed by combining the 2 subjects. If you see the GATE 2020 EE paper, you can see that they have framed quite a few questions combining multiple subjects. Now we discuss each module of Electrical Machines one by one. Each module is almost as big as a single subject so a student should devote at least 2-3 months on machines if they want to cover all the concepts completely.
MAGNETIC CIRCUITS (Electrical Machine for GATE & ESE)
This is a very basic topic and it will help you understand further topics in a better way. You must understand the concepts of MMF, flux, flux density, reluctance, difference of flux in a ferromagnetic core compared to an air core, and most importantly reluctance. Also, you must cover the topics of leakage flux and fringing.
Next, you should cover how to calculate reluctance for different configurations like series, parallel, and their combinations which may involve ferromagnetic core as well as air gaps. Also, you need to know calculate flux and flux density in the paths. Also, you need an idea of energy stored in air gaps and lifting forces developed in those.
The last topic in this module is the BH curve. This topic is very important for understanding the operation of any machine. You can refer to the appendix to Electrical Machinery by PS Bimbhra for this topic or you can purchase the Electrical Machine 3.0 Course delivered by Sohail Sir on the Neospark App
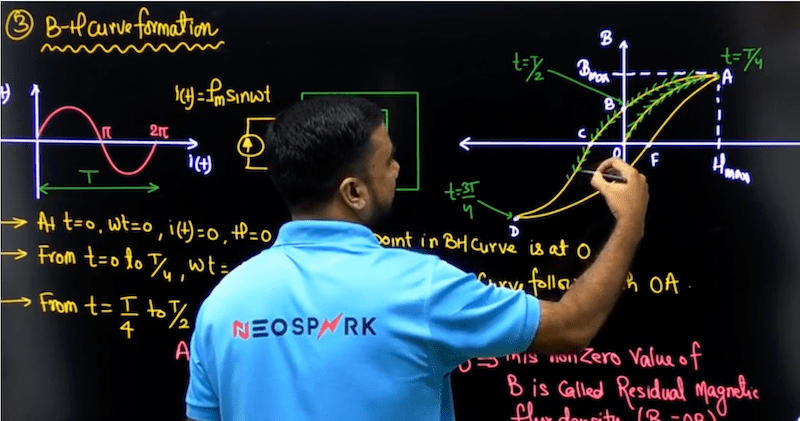 |
TRANSFORMERS (Electrical Machine for GATE & ESE)
This is one of the biggest modules of Electrical Machines and can be roughly divided into 2 parts – single phase and 3 phase.
We start with a single-phase transformer. The first part of it deals with construction with various aspects of core and shell types. Then we deal with the concept of dot polarity and its application with respect to transformers. Then we consider an ideal transformer and study its working. Then we consider a practical transformer and incorporate the effects of various non-idealities on its working. We develop phasor diagrams and equivalent circuits in all these cases by modeling the non-idealities accordingly. Finally in this part, we learn about impedance transformation from one side to another and then how a transformer can be used for impedance matching. Also after this, we study the modeling of a transformer as a magnetically coupled circuit and then learn to compute the various inductances in terms of transformer dimensions.
Next, we study the various kinds of losses in a transformer and how they are affected by changing operating conditions. Then we study various kinds of tests to calculate the losses in a transformer. With regards to gate only no load and short circuit tests are needed while an ESE aspirant should also cover Sumpner’s test.
Then comes the very important topics of efficiency and voltage regulation. In this regard, the concept of per-unit values needs to be studied although they are covered in greater detail later in Power System. In efficiency, both power efficiency and all-day efficiency need to be studied. Also, the condition of maximum efficiency is important. Under voltage regulation, the conditions of maximum, minimum, zero, and negative voltage regulation need to be understood. Also how voltage regulation is different for power and distribution transformers has to be clear. After this, we understand how a transformer is rated and how changing the dimensions of a transformer can vary various factors. This portion is highly important from a numerical point of view.
The next topic is the excitation phenomenon in transformers. Here we study the effects of harmonics on transformer operation in particular flux, emf, and magnetizing current. The concept of the BH curve should be very clear to understand this part. Then we study the inrush phenomenon. You can read these from the books of Nagrath and Kothari.
This brings an end to single-phase transformers. We now move to 3-phase transformers. IN aspirants should skip these and move to 3 3-phase induction motor and after that to the conclusion.
Before starting 3-phase transformers, make sure to fully master the concepts of line and phase currents, line and phase voltages, the effect of phase sequence on them, and power in 3-phase completely otherwise you can’t understand 3-phase transformers.
First, we study 3 phase transformer construction which covers 3 limb core and 5 limb shell types and their characteristics. After that, we study the various transformer connections and classify them into different phasor/vector groups. We also cover the special case of open delta. Note that Scott connection and zigzag connections are not included in GATE but should be studied for ESE. Finally, we study the excitation phenomenon in 3 3-phase transformers as well and investigate the presence of harmonics in various line and phase quantities depending on transformer connection. Very conceptual questions can be framed from 3 phase transformers and hence should be studied very thoroughly. You can refer to the book of Nagrath Kothari or the Generalized theory of electrical machines by Bimbhra for this portion.
Then we take a very important topic in transformers which is common to both single and 3 phase is the concept of parallel operation and it is highly important. The different conditions for parallel operation should be understood and out of them, we should know which conditions are necessary and which are desirable. The equations for load sharing should be clear under various cases. You can refer to both the books of PS Bimhhra for this.
The last topic in this module is autotransformer. Here we study the principle of operation of an autotransformer and compare it with a 2-winding transformer. Next, we analyze the different cases where a 2-winding transformer is reconnected to an autotransformer and compare the performance with the original 2-winding transformer. You can read Electrical Machinery by PS Bimbhra for this portion and also a generalized theory of electrical machines for a brief idea of 3 phase autotransformer. This brings the module to a close.
If you are planning by self self-study then you have to go through this topic from books or free YouTube lectures. But if you want to study this topic in a structured way then Enroll in the Electrical Machine 3.0 Course on Neospark App.
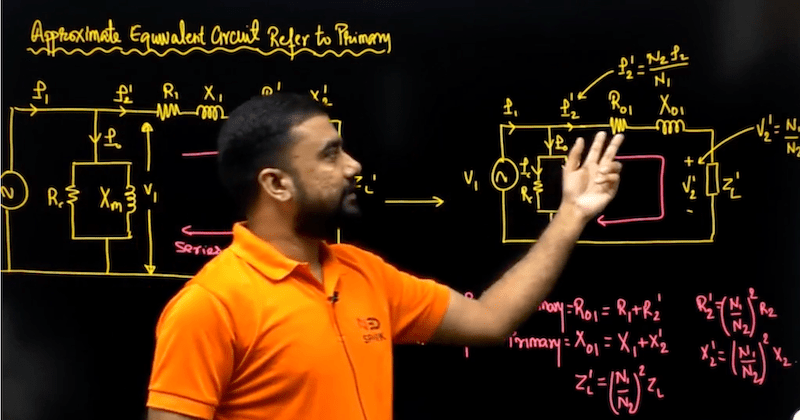 |
 |
ELECTROMECHANICAL ENERGY CONVERSION PRINCIPLES (Electrical Machine for GATE & ESE)
This is a small module and relatively less important in terms of questions being asked in GATE.
This module deals with the basic concept of conversion of electrical energy to mechanical energy and vice versa via a coupling magnetic field. The various media of stored, dissipated, and lost energy are analyzed here. Then we study the particular cases of singly and doubly excited systems and learn to find the acting forces and torques. Also, we need to cover the different kinds of energy stored in each case. While studying this module, focus should be kept on the particular concept of co-energy and how it is affected by the saturation of the magnetic circuit. For this part, a student can refer to the book by Nagrath and Kothari. Or Enroll in the Machine 3.0 Course on the Neospark App.
DC MACHINES (Electrical Machine for GATE & ESE)
This is a very simple and scoring topic and less time-consuming compared to other modules. First, you need to cover the construction of DC machines. While covering construction, for GATE, there is no need to go into details of armature winding. Only the basic concepts of lap and wave for simplex and multiplex with respect to the number of parallel paths and current in each coil for each case would be enough. However, an ESE aspirant should cover these in detail. One can refer to Electrical Machinery by PS Bimbhra for these parts.
Next, we dive into the principle of operation of generator and motor. We study the EMF equation and the torque equation. Then we learn to classify the DC machines based on the methods of excitation and derive circuit models for them accordingly. This is the most important part as most problems of GATE can be solved by the circuit model only. Next, we cover the process of build-up of emf in a generator and its necessary conditions. This also includes important concepts like critical speed and critical resistance. These concepts are covered by Bimbhra or Nagrath.
The next concept to study is commutation. The different types of communication and concepts of under and over-commutation need to be covered. It is followed by the concept of armature reaction and its consequences. In this regard, brush shift, interpoles, and compensating windings are important as numerical are possible from there. It should be noted that waveforms of different fluxes and MMF before and after compensation of armature reaction although not directly included in the gate syllabus are needed for a better understanding of this part. This part can be covered by PS Bimbhra.
Next, the load characteristics of both generator and motor for each type should be studied and analyzed. The effect of armature reaction on each of these characteristics should be analyzed as well. The next part which is very important is speed control of the DC motor. The concept of speed regulation plus each method of speed control needs to be analyzed. The best reference book in this regard would be Nagrath and Kothari. The concepts of starting and braking of DC motor which come after this are not that important.
The final part of this module is losses and efficiency. The case for both the generator and motor needs to be studied for efficiency along with the classification of losses. The condition for maximum efficiency should be noted. The methods for testing losses are not important.
If you are planning to self-study then you have to go through these topics from books or free YouTube lectures. But if you want to study this topic in a structured way then Enroll in the Electrical Machine 3.0 Course on the Neospark App.
3 PHASE INDUCTION MACHINES (Electrical Machine for GATE & ESE)
This module is also included in the GATE IN syllabus. Each part is explained step by step. Any of the books mentioned in the introduction can be used for this module as a reference.
First, the concept of a rotating magnetic field needs to be understood very well, and along with it the concept of slip. The same concept of slip needs to be understood for an inverted induction motor as well.
The next portions are the most important ones in this module and 90% of questions are asked from here. We cover the rotor equivalent circuit of the 3-phase induction motor in this section and assuming standstill rotor induced emf to be fixed, derive current, torque, and power factor. The variation of these quantities with slip is highly important. Also, approximate analysis around the operating point is very important. In this regard, the power flow diagram needs to be studied along with various kinds of losses. The different quantitates like air gap power, electromagnetic torque, and shaft torque should be very clear as well.
Next, we model the entire equivalent circuit of the motor including the stator and from it the conditions of maximum torque and power. This is also called the IEEE model. Also, we study the torque-slip and power-slip characteristics. From the torque-slip characteristics, we analyze the stability of the motor at different operating points.
The next part covers the no-load and blocked rotor tests along with a circle diagram which is not important for GATE but should be done for ESE.
Starting of 3 3-phase induction motor is a very important topic and the various starting methods and the corresponding formulae for starting current and starting torque should be known well. Electrical Machinery by PS Bimbhra is the best reference here. Then we arrive at the different methods of speed control of 3-phase induction machines which should be very easily covered if the torque-slip relations are well known. This portion can be covered in Nagrath and Kothari’s book. Braking methods of 3-phase IM are not very important.
Next, we cover the different kinds of 3-phase IM and their constructional features. They include slip ring or wound rotor IM and squirrel cage IM (SCIM). SCIM can be further classified into deep bar rotor and double cage rotor types. They can be covered in Nagrath and Kothari’s book.
Next, we cover the concept of space and time harmonics in 3-phase IM along with the concepts of crawling, cogging, and skewing. These can be covered in the Generalized Theory of Electrical Machines by Bimbhra.
Finally, the last topic in this regard is 3 3-phase induction generator which includes an isolated induction generator. This is not important for GATE but should be done for ESE.
SINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MACHINES (Electrical Machine for GATE & ESE)
This module covers a single-phase induction motor and should be simple if the previous module is done properly. First, the concept of double-revolving field theory should be understood. Then from this concept, we frame the equivalent circuit of a single-phase induction motor and calculate various parameters related to current, torque, power, and losses. This part can be covered in the book Basic Electrical Engineering by Mittle and Mittal. This book is not mentioned in the introduction as it is not good enough for other modules but can prove useful here.
The next part is very important. First, we study the torque-slip characteristics followed by the various types of single-phase induction motors based on starting methods like capacitor start, capacitor run, etc. The book mentioned before covers this part pretty well. Finally, we study the condition of maximum torque in a single-phase induction motor. This part is very important and can be covered in the Generalized Theory of Electrical Machines by Bimbhra. This concludes this module.
SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES (Electrical Machine for GATE & ESE)
Finally we arrive at the module which is the bane for most aspirants. Here every topic is broken down step by step to make it simpler. It is necessary that before starting this module, one should be very comfortable with drawing phasor diagrams. References for this module would be the book of Nagrath and Kothari along with Electrical Machinery with PS Bimbhra as no single book would be sufficient in this regard.
First we cover the concept of emf in synchronous machine, pitch factor and distribution factor. Also we analyze how harmonics are affected by choosing these factors accordingly. Also we study the types of armature windings. Next we move on the concept of flux per pole including the effect of harmonics. Then we study the concept of electrical and mechanical angle.
Then we revise the already studied concept of rotating magnetic field. Then we study the different types of rotors namely salient pole and cylindrical. Note that construction of synchronous machines is not important from GATE point of view.
Then we study the various flux mmf phasor diagrams for different modes of operation of synchronous machines and also along with it the various natures of armature reactions based on operating power factor. They can be demagnetizing, magnetizing, cross-magnetizing or any combination of these.
The various methods of calculating voltage regulation of alternators are not at all needed for GATE. Voltage regulation if asked can be calculated easily from the phasor relationship of various quantities of an alternator. But these need to be studied in detail for ESE conventional paper.
Next we study the equivalent circuit of cyclindrical rotor synchronous machines along with phasor diagrams for both alternator and motor under both leading and lagging conditions. Note while studying equivalent circuit, we also study in detail the different reactances like leakage reatance, armature reactance and their sum which is synchronous reactance.
The most important part of this module are the phasor relations between induced emf, terminal voltage and armature current used for problem solving. Note that these are complex numbers which can’t be calculated using the calculator on the screen. Scientific calculator is not allowed. So the corresponding scalar equations must be known. This would come useful later for Power Systems as well. Practice is needed here for numericals.
The next part deals with various characteristics and terms like open circuit characteristics, short circuit characteristics, short circuit ratio, zero power factor characteristics, Potier triangle, load characteristics, field compounding characteristics, V curve and inverted V curve.
Power angle equations for cylindrical rotor which come after this are highly important for GATE. The various formulae for active and reactive power and maximum power conditions should be covered. After that assuming zero armature resistance, we study power angle curve and excitation of cylindrical rotor synchronous machines based on reactive power at the electrical terminals. The cases related to loss of excitation and variation of load or excitation should be studied meticulously as they are highly important.
The next portion deals with behavior of an alternator connected to an infinite bus bar and frequency power characteristics of an alternator. Then we study the parallel operation of alternators, load sharing and synchronization.
After this, the topic of salient pole synchronous machines has to be covered. For this, first the two reaction theory should be covered and the phasor diagrams for salient pole alternator as well as motor should studied for leading as well as lagging power factor cases. Here as well, for numerical point if view, the scalar forms of the phasor equations should be known.
Similarly, power angle equations must be known and the concepts of electromagnetic and reluctance power as well. Then like cylindrical rotor case, here too we study the P-δ curve and the various cases related too loss of excitation. The last topic under salient pole machines is slip test which is not important for GATE. It is sufficient to know the formulae of Xd and Xq.
The next topic under this module are the concepts of synchronizing torque and power for both cylindrical rotor and salient pole rotor machines. This is very important from numerical point of view.
The other remaining topics to be studied are harmonics in synchronous machines, development of torque, hunting, damper windings and starting of synchronous motors. Also use of synchronous condenser as a power factor correction device.
This sums up the module and completes GATE syllabus.
SPECIAL MACHINES (Electrical Machine for GATE & ESE)
This portion is not included in GATE and only is in ESE. This covers servo and stepper motors. They can be covered from the book by Nagrath and Kothari or Generalized Theory of Electrical Machines by Bimbhra.
CONCLUSION
The most important aspect of this subject is revision and practice.
You can check out Neospark App for Machine 3.0 Lecture.
You can check out the revision videos on Neospark App for core subjects
If you are planning by self-study then you have to go through these topic from books or free YouTube lectures. But if you want to study these topic in structured way then Enroll in Electrical Machine 3.0 Course on Neospark App.
Best it luck for your preparation and may out come out with flying colours.

